On May 1, 2025, the Japan Fair Trade Commission (the "JFTC") published "Enforcement of the Antimonopoly Act in FY2024" (the "Report")1. The Report highlights a significant increase in the number of enforcement cases, marking the highest volume in five years, which reflects the JFTC's ongoing commitment to strengthening the enforcement of the Antimonopoly Act. This article provides an overview of the report's key points.
1. Increasing Trend in Legal Measures
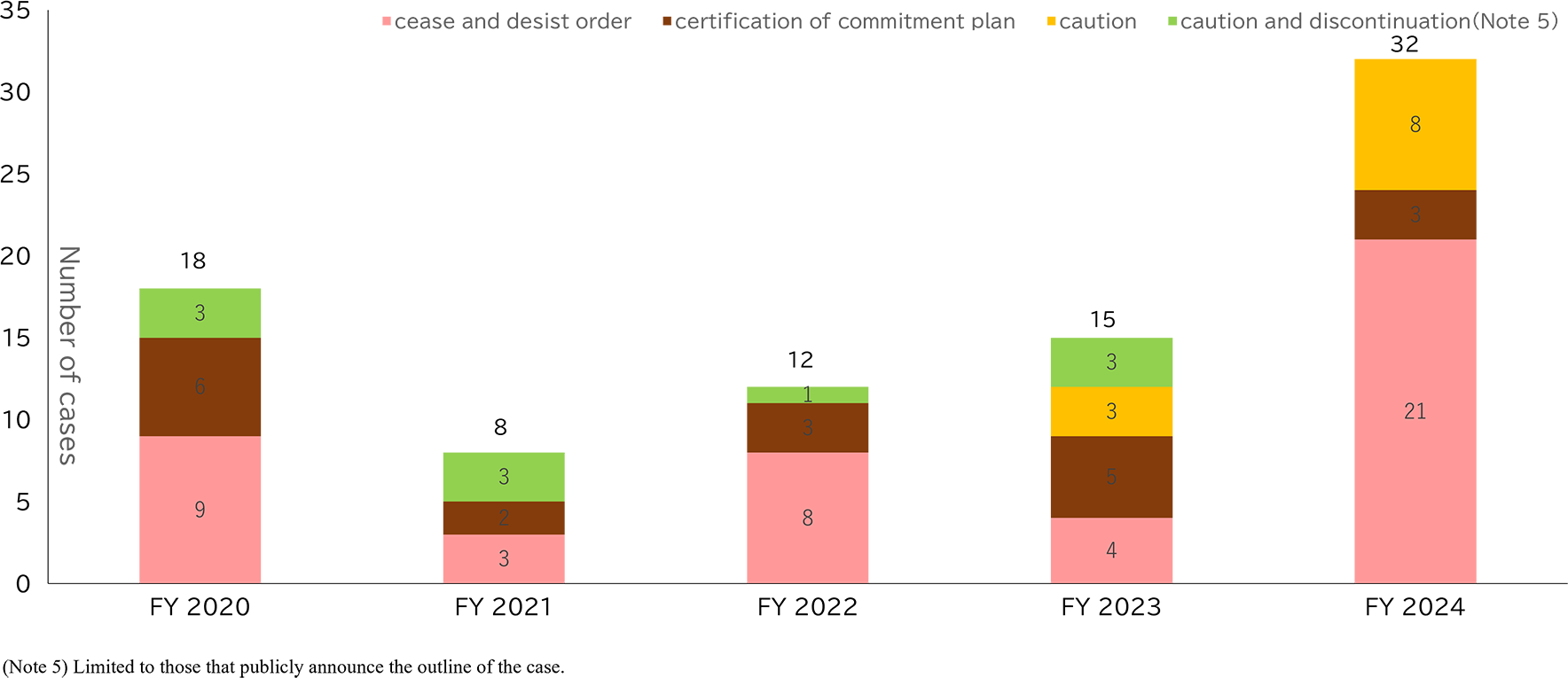
In FY 2024, the JFTC implemented a total of 24 legal measures, including 21 cease-and-desist orders and 3 commitment procedures2. This represents a substantial increase from the 9 measures taken in the previous fiscal year.
Figure 1: Changes in the number of legal actions
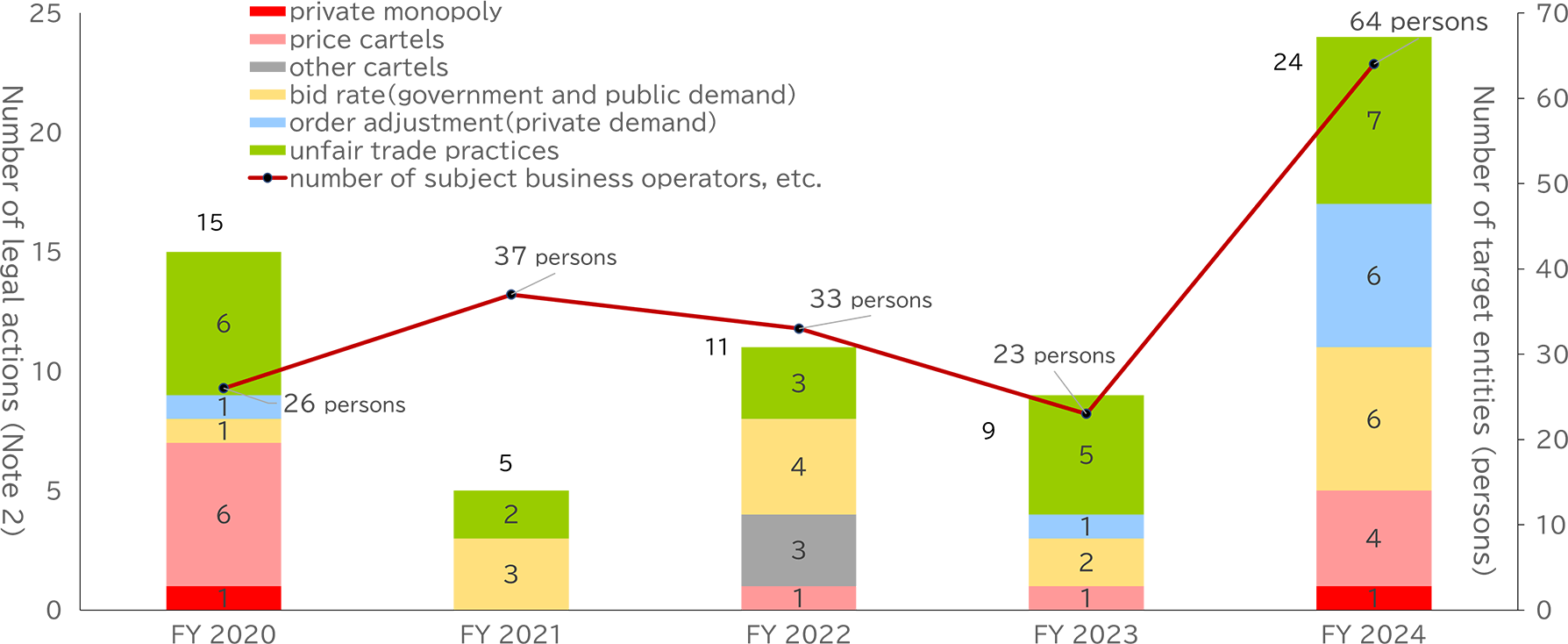
Among the noteworthy cases were the stringent actions taken against large-scale price cartels and bid-rigging schemes. For instance, in a case involving insurance companies engaging in pre-arranged pricing of premiums and bid-rigging for municipal insurance contracts, the JFTC issued surcharge payment orders totaling approximately 2.1 billion yen against 5 violators.
It is also important to note that, despite commitment procedures generally being applied to unfair trade practices since Rakuten, Inc.'s case in 20193, 5 cease-and-desist orders against unfair trade practices have been issued in FY 2024.
Additionally, the JFTC issued 8 warnings, which is an increase compared to the previous fiscal year. Notably, two of these warnings concerned "resale price maintenance", which is a type of unfair trade practice involving explicit price restrictions.
Figure 2: Changes in the number of cease and desist orders, certification of firm commitment plans, warnings, etc.
1 https://www.jftc.go.jp/file/5/1a.pdf (In Japanese): According to JFTC’s press release, the English translation will be posted at a later date.
2 This is one of the administrative measures available under the Antimonopoly Act. If a commitment procedure, approved by the JFTC based on an application from a business operator, is not implemented as certified, the JFTC may revoke any approvals granted and resume its prior investigation.
2. Addressing the IT and Digital-Related Sectors
To promote the swift restoration of competition in the IT and digital-related sectors, the JFTC adopted tailored, effective measures for each case. Examples include:
- MC Data Plus Co., Ltd.: The JFTC issued a cease-and-desist order confirming that the company had stopped preventing its users from switching to competitors’ services.
- Google LLC: In a case involving restrictions on the provision of essential technologies for mobile syndication transactions4 in connection with search-linked advertising services provided to Yahoo Japan Corporation, the JFTC approved a commitment plan requiring Google to cease its restrictive practices and ensure thorough notification to relevant parties.
The JFTC has also established a specialized IT and Digital Task Force to investigate suspected violations of the Antimonopoly Act violations in these sectors. In FY 2024, the task force received 110 reports of potentially unlawful conduct.
3 https://www.jftc.go.jp/en/pressreleases/yearly-2019/October/191025.html
4 This describes transactions in which a business operator distributing search-linked advertisements receives advertising space from website operators or other parties, distributes search-linked advertisements in that space, and shares a portion of the revenue generated by the advertisements with the relevant parties.
3. Other Observed Trends
Leniency applications for surcharge reductions totaled 109 in FY 2024, a decrease from the previous year yet still a substantial number. 53 businesses were granted leniency and 16 legal measures were applied under the leniency program, both of which exceeded the previous year's figures. Our view is that the increase is due to applications submitted during the previous fiscal year related to the insurance company case mentioned in 1., which applications were processed in FY 2024.
Furthermore, the leniency system that allows for reductions in surcharges based on cooperation with the JFTC investigations was applied to 13 cases involving 29 businesses, marking an increase compared to the previous fiscal year.
In light of sharp rise in labor costs, raw material prices, and energy expenses, the JFTC issued 41 cautions in response to requests related to the passing on of price increases, as well as to practices by shippers in logistics transactions.
4. Conclusion
The JFTC's enhanced attitude towards the enforcement of the Antimonopoly Act is evident, as the number of legal measures is expected to continue increasing or remain the same. The JFTC is also intensifying its enforcement of the Subcontract Act5, and warnings that are subject to public disclosure are showing a similar upward trend. In view of these trends, we believe that businesses should prioritize reviewing and strengthening their compliance frameworks while remaining vigilant against reputational risks.
5 The Subcontract Act is scheduled to be revised on January 1, 2026, with the aim of strengthening enforcement, and the name of the law is also scheduled to be changed to "the Act on the Promotion of Subcontracting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises."

